Discover 20 hidden attractions, cool sights, and unusual things to do in Durham (United Kingdom). Don't miss out on these must-see attractions: Durham Cathedral, Durham Castle, and Oriental Museum. Also, be sure to include Prebends Bridge in your itinerary.
Below, you can find the list of the most amazing places you should visit in Durham (England).
Table of Contents
Durham Cathedral
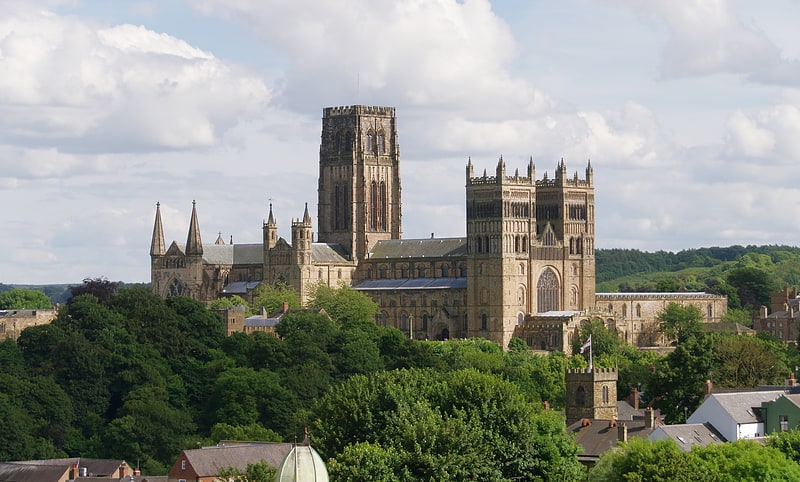

Iconic, vaulted Romanesque building. The Cathedral Church of Christ, Blessed Mary the Virgin and St Cuthbert of Durham, commonly known as Durham Cathedral and home of the Shrine of St Cuthbert, is a cathedral in the city of Durham, England. It is the seat of the Bishop of Durham, the fourth-ranked bishop in the Church of England hierarchy.
The present Norman era cathedral had started to be built in 1093, replacing the city's previous 'White Church'. In 1986 the cathedral and Durham Castle were designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Durham Cathedral's relics include: Saint Cuthbert's, transported to Durham by Lindisfarne monks in the 800s; Saint Oswald's head and the Venerable Bede's remains.
The Durham Dean and Chapter Library contains: sets of early printed books, some of the most complete in England; the pre-Dissolution monastic accounts and three copies of Magna Carta.
From 1080 until 1836, the Bishop of Durham held the powers of an Earl Palatine. In order to protect the Anglo-Scottish border, powers of an earl included exercising military, civil, and religious leadership. The cathedral walls formed part of Durham Castle, the chief seat of the Bishop of Durham.
There are daily Church of England services at the cathedral, Durham Cathedral Choir sing daily except Mondays and holidays, receiving 727,367 visitors in 2019.[1]
Address: The College, DH1 3EH Durham
Durham Castle
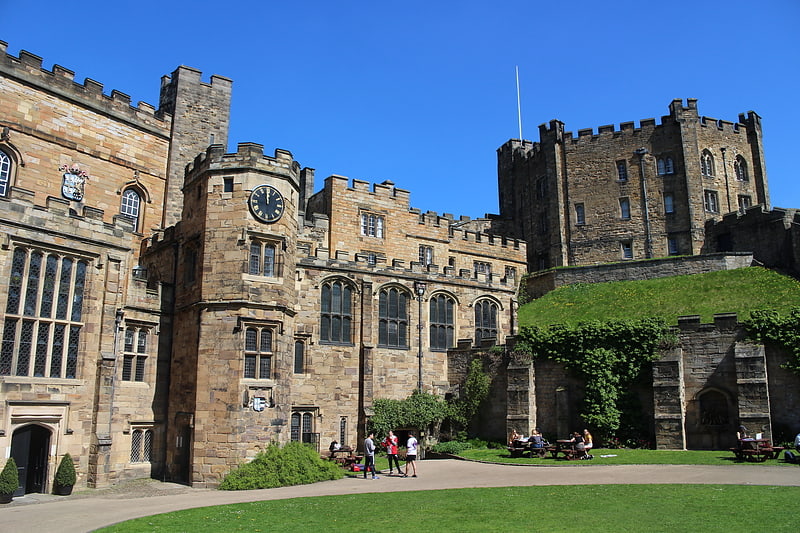

Castle in Durham, England. Durham Castle is a Norman castle in the city of Durham, England, which has been occupied since 1837 by University College, Durham after its previous role as the residence of the Bishops of Durham. Designated since 1986 as a cultural World Heritage Site in England, along with Durham Cathedral, the facility is open to the general public to visit, but only through guided tours, since it is in use as a working building and is home to over 100 students. The castle stands on top of a hill above the River Wear on Durham's peninsula, opposite Durham Cathedral.[2]
Address: Palace Green, DH1 3RW Durham
Oriental Museum
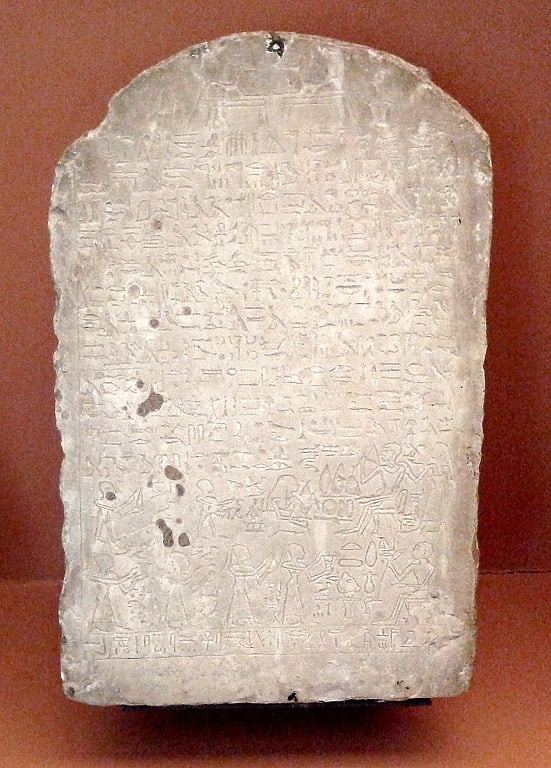

The Oriental Museum, formerly the Gulbenkian Museum of Oriental Art and Archaeology, is a museum of the University of Durham in England. The museum has a collection of more than 23,500 Chinese, Egyptian, Korean, Indian, Japanese and other far east and Asian artefacts. The museum was founded due to the need to house an increasing collection of Oriental artefacts used by the School of Oriental Studies, that were previously housed around the University. The Museum's Chinese and Egyptian collections were 'designated' by the Museums, Libraries and Archives Council, now the Arts Council England as being of "national and international importance".[3]
Address: Durham, County Durham DH1 3TH, DH1 3TH Durham
Prebends Bridge
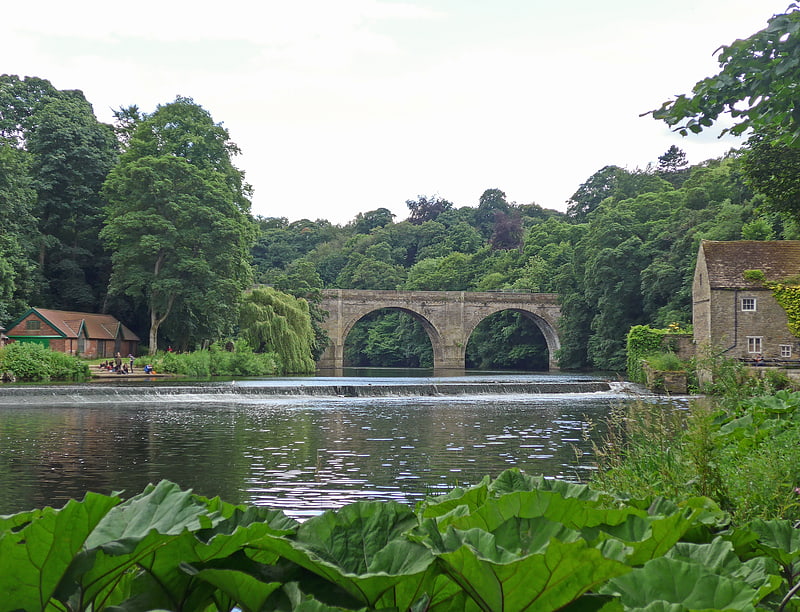

Arch bridge in Durham, England. Prebends Bridge, along with Framwellgate and Elvet bridges, is one of three stone-arch bridges in the centre of Durham, England, that cross the River Wear.[4]
Durham University Museum of Archaeology
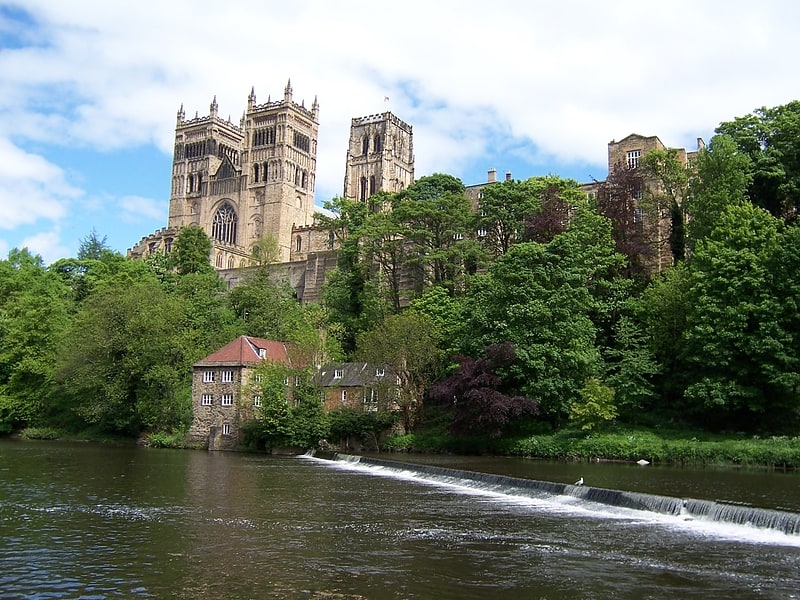

The Museum of Archaeology, founded in 1833, is a museum of the University of Durham in England. The museum has collections ranging from the prehistoric, Ancient Greece, Roman to Medieval.[5]
Durham Town Hall
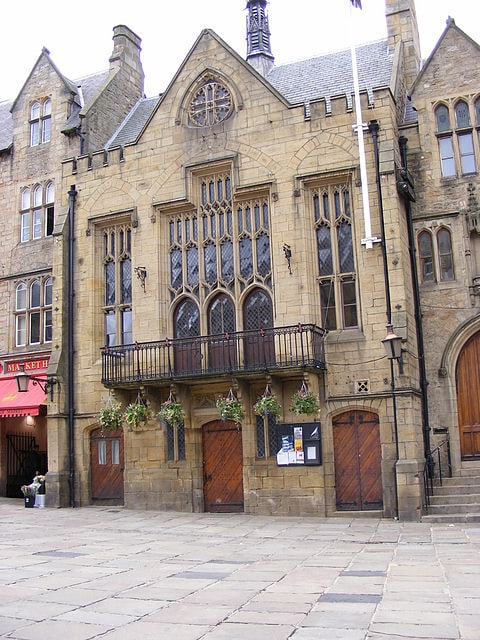

Heritage building in Durham, England. Durham Town Hall is a municipal building in the Market Place, Durham, England. It is a Grade II* listed building.[6]
Address: Market Place, Durham
Finchale Priory
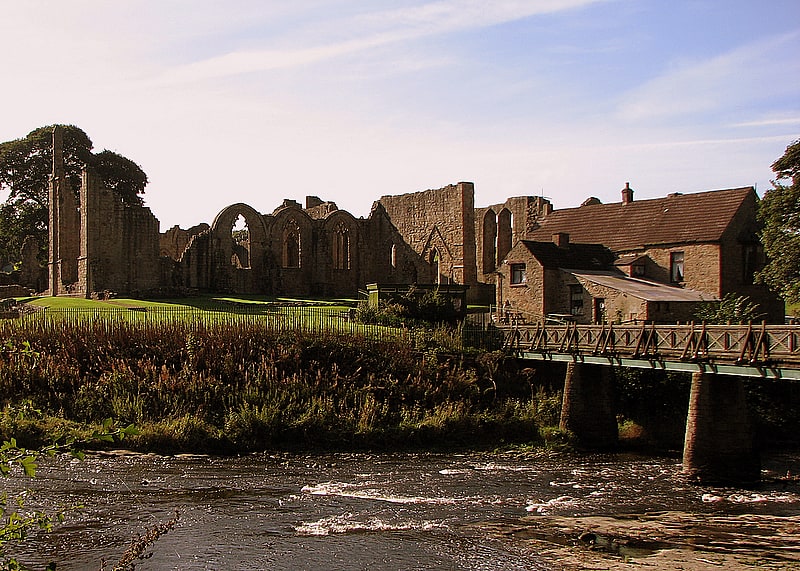

Priory. Finchale Priory sometimes referred to as Finchale Abbey was a 13th-century Benedictine priory. The remains are sited by the River Wear, four miles from Durham, England. It is a Grade I listed building.[7]
Address: Finchale Avenue, DH1 5SH Durham
Elvet Bridge
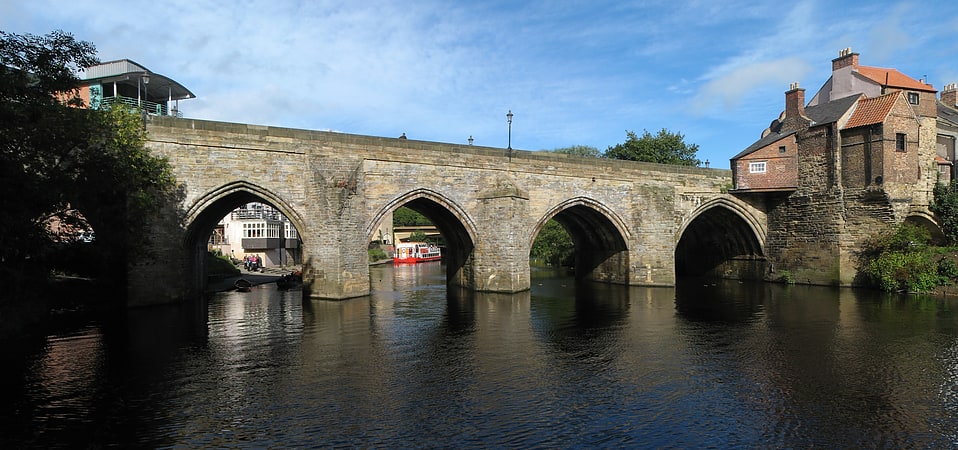

Arch bridge in Durham, England. Elvet Bridge is a medieval masonry arch bridge across the River Wear in the city of Durham, in County Durham, England. It links the peninsula in central Durham and the Elvet area of the city, and is a Grade I listed building.[8]
Address: 10 Elvet Bridge, Durham
Framwellgate Bridge

Arch bridge in Durham, England. Framwellgate Bridge is a mediaeval masonry arch bridge across the River Wear, in Durham, England. It is a Grade I listed building.[9]
St Cuthbert's Church
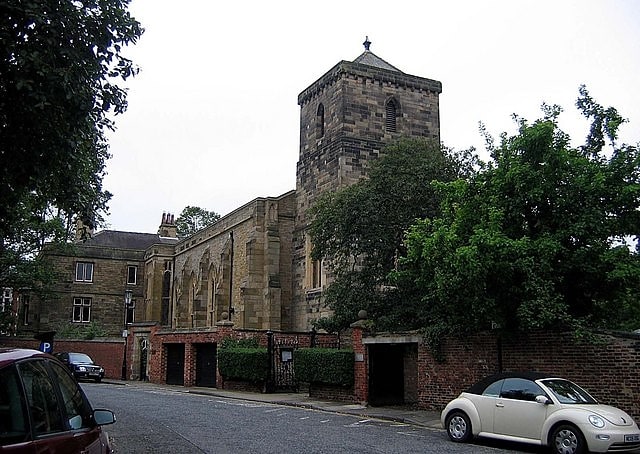

Parish church in Durham, England. St Cuthbert's Church is a Roman Catholic parish church in Durham, England. It was opened on 31 May 1827 to replace two previous chapels, one run by the secular clergy and the other by the Jesuits. It is also the home of the Durham University Catholic Chaplaincy and Catholic Society. From 2012 to 2016 the parish was entrusted, along with the chaplaincy, to the Dominican Order, and its congregation has since maintained the Dominicans' influence. The church is a protected building, being part of the Elvet Green Conservation Area. It is named for St Cuthbert of Lindisfarne, the 7th century bishop, healer and patron of Northern England.[10]
Address: Old Elvet, Durham
Assembly Rooms Theatre
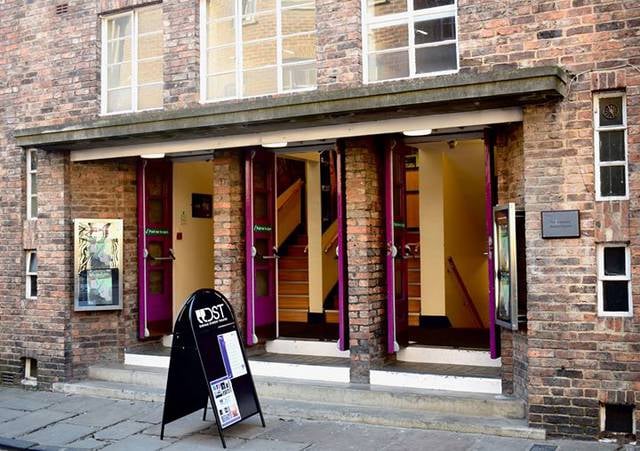

The Assembly Rooms Theatre is a historic 220-seat proscenium arch theatre located in the centre of Durham. During term time, it primarily hosts the work of Durham Student Theatre's 27 resident companies, and also presents the work of external and touring companies at other points in the year. The theatre is managed by Experience Durham, a department of Durham University, and is run by two full-time members of staff alongside a team of student volunteers.[11]
Address: 40 North Bailey, Durham
Durham Museum and Heritage Centre
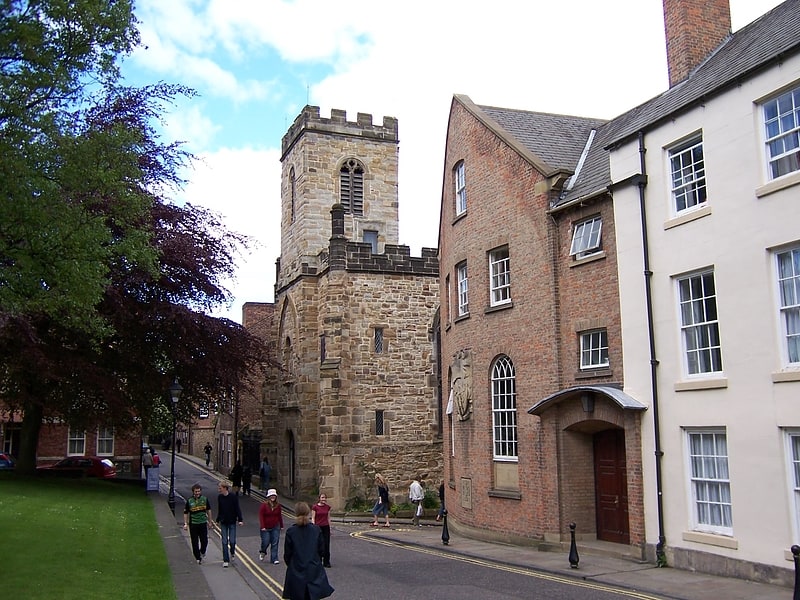

Museum in Durham, England. Durham Museum and Heritage Centre is a museum in Durham, England. It details the history of the City of Durham from medieval times to the present day. The museum is located in the redundant church of St Mary-le-Bow, close to the World Heritage Site of Durham Cathedral and Durham Castle. It is bounded on the north and east by Hatfield College; on the south by Bow Lane, and the west by North Bailey.
The museum contains a variety of objects, models, pictures and audio-visual displays. These exhibitions provide the visitor with an overview of life, labour and leisure in this ancient fortified city, centre of pilgrimage and capital of the Prince Bishops of Durham. The museum also features a centre for making brass rubbings.[12]
Address: Durham World Heritage Site Visitor Centre, DH1 3HB Durham
Kingsgate Bridge
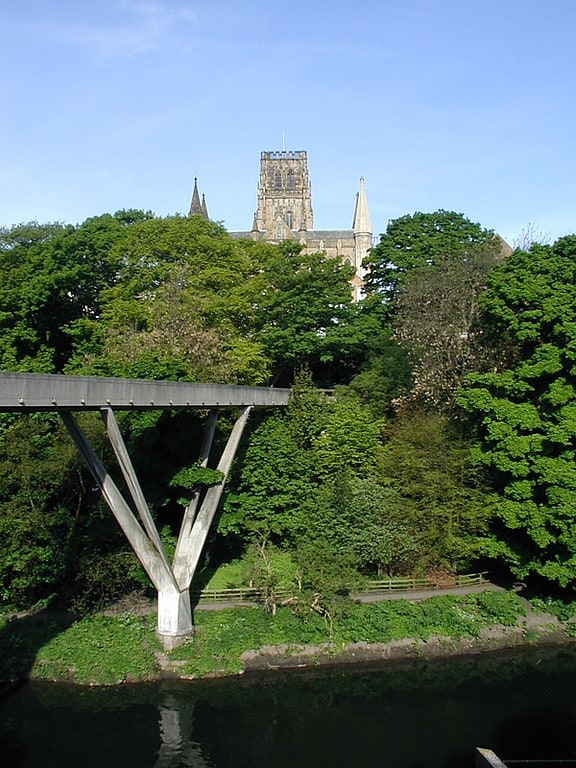

Bridge. Kingsgate Bridge is a striking, modern reinforced concrete construction footbridge across the River Wear, in Durham, England. It is a Grade I listed building. It was personally designed in 1963 by Ove Arup, the last structure he ever designed. Kingsgate Bridge connects Bow Lane on the historic peninsula in the centre of Durham to Dunelm House on New Elvet, and opened in 1966. Kingsgate Bridge is thought to have been one of Arup's favourite designs of all, he having spent many hours working on every detail of the plans.
Its construction was unusual. The two halves were each built parallel to the river, then rotated through 90° to make the crossing. The meeting point of the two halves is marked by a simple bronze expansion joint using a linear gear bearing.
In 1965, the bridge was the winner of the Civic Trust Award.
In 1993, it won Certificate of Outstanding Performance (Mature Structures Category) of the Concrete Society.
A bust of Arup, cast in resin, was installed on the side of Dunelm House, the students' union building adjacent to the bridge, in September 2011. The sculpture is a copy of a 1987 bust by Diana Brandenburger, held by the National Portrait Gallery. It is a replacement for a previous copy of the same bust, in bronze, which was unveiled by Karin Perry, Arup's daughter, on 16 April 2003, the 108th anniversary of Arup's birth, but which was stolen from its plinth during the summer of 2006.
During a university RAG Week in the late 1960s students suspended a car beneath the bridge.[13]
Durham University Botanic Garden
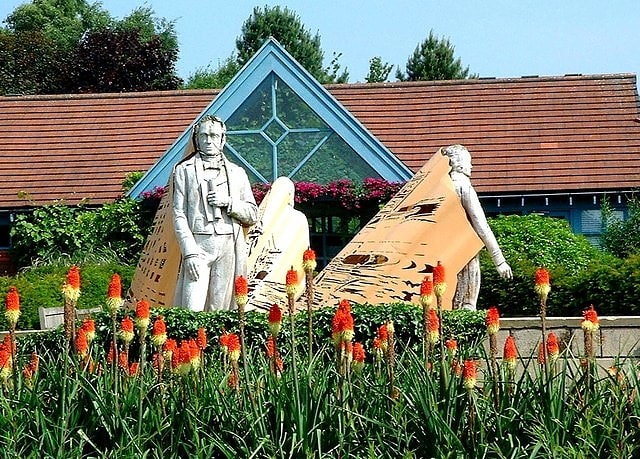

Botanical garden in Durham, England. The Durham University Botanic Garden is a botanical garden located in Durham, England. The site is set in 25 acres of mature woodlands in the southern outskirts of the city. The botanic gardens have been located on their present site since 1970 before being officially opened in 1988 by the then Chancellor Dame Margot Fonteyn and now attract some 80,000 visitors annually.[14]
Address: Hollingside Lane, DH1 3TN Durham
St Giles Church
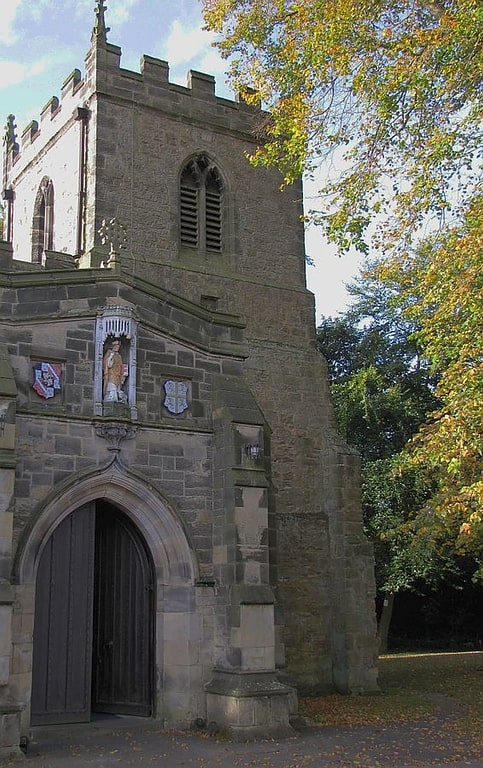

Church in Durham, England. St. Giles Church is a grade I listed parish church in Gilesgate, Durham, England.
The church was constructed as the hospital chapel of the Hospital of St Giles and was dedicated in on St Barbara's Day, June 1112 by Bishop Flambard to "the honour of God and St Giles". The church became caught up in an 1140 dispute over the bishopric of Durham following the usurpation of the diocese by William Cumin, Chancellor of King David I of Scotland. William of St. Barbara, the rightly elected Bishop, was forced to retreat to, and fortify, the church after his abortive entry into Durham was beaten back by Cumin's men. In response Cumin's men destroyed the hospital, which was later refounded at nearby Kepier.
Bishop Puiset later extended the church to reflect its role at the centre of a growing parish, and the current font is believed to date from this time. The church was appropriated to Kepier Hospital which acted as rector, receiving tithes and with the advowson (right to appoint a vicar), appointing a parochial chaplain to minister to the needs of the parish.
John Heath, the Elizabethan owner of the Kepier estates, Gilesgate and Old Durham is buried in the church.
The ecclesiastical parish of St Giles was divided in 1852 with the creation of a new Belmont parish, served from church of St Mary Magdalene, Belmont and covering Belmont, Gilesgate Moor and New Durham.
St Giles Church retains some of Flambard's original building (primarily the north wall) and most of Puiset's additions. Minor restoration and three large windows inserted into the south wall in 1828. The church was restored and extended in 1873-1876 as the parish continued to grow.
The Revd Canon Dr Alan B. Bartlett is the current vicar of St Giles since Summer 2008.[15]
Cosin's Library
Library in Durham, England. Bishop Cosin's Library, originally the Episcopal Library or Bibliotheca Episcopalis Dunelmensis, is an historic library founded in 1669 in Durham, England. Owned by the University of Durham, the library is open to the public.[16]
Durham Indoor Market
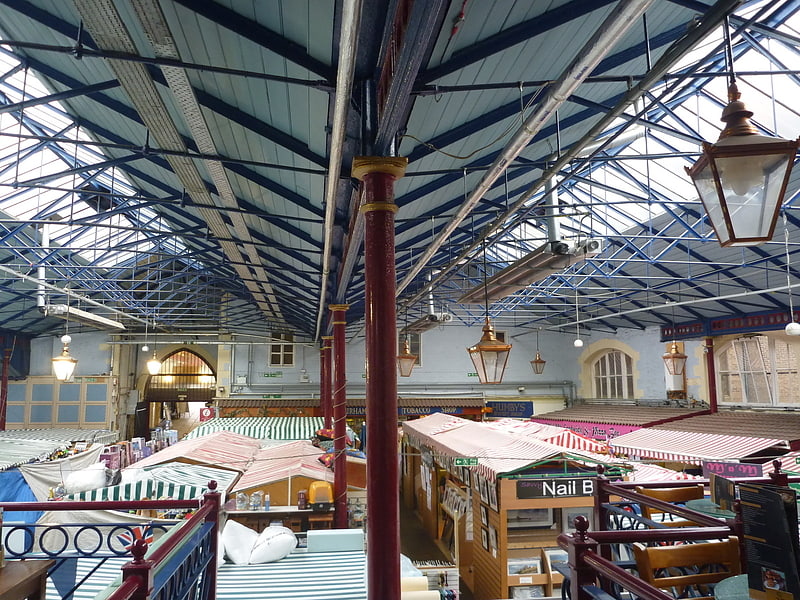

Durham Indoor Market is a covered market located off the Market Place in the City of Durham, England.[17]
St Margaret's Church

Parish church in Durham, England. St Margaret's Church Durham is an active parish Church situated on Crossgate in the city of Durham in the North-East of England. The building is Grade I listed and substantial parts date from the 12th century; the compact yet spacious interior has a pleasing asymmetry, which reveals different stages in the building's development.[18]
St Nicholas Church
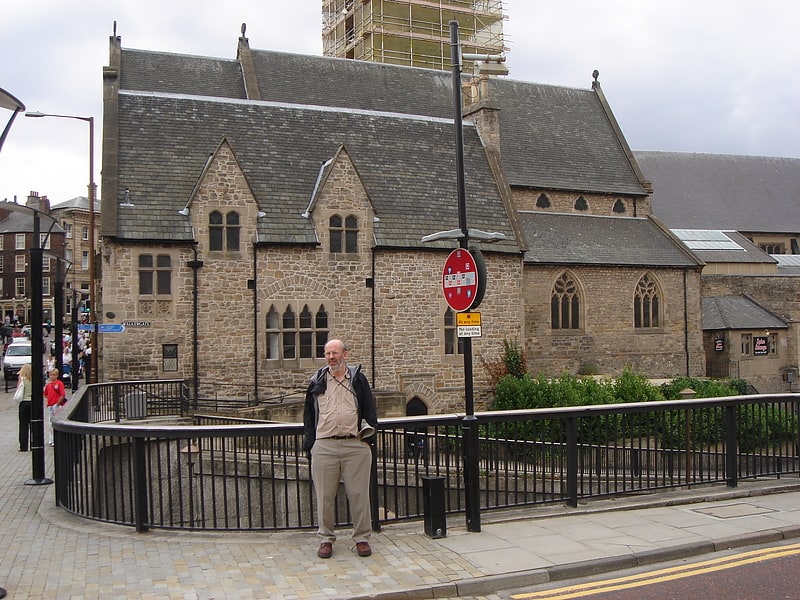

Anglican church in Durham, England. St Nicholas Church, commonly known as St Nics, is a Church of England place of worship located on Durham marketplace and is the city's civic church. The church stands in the open evangelical tradition of the Church of England.[19]
St Oswald's Church
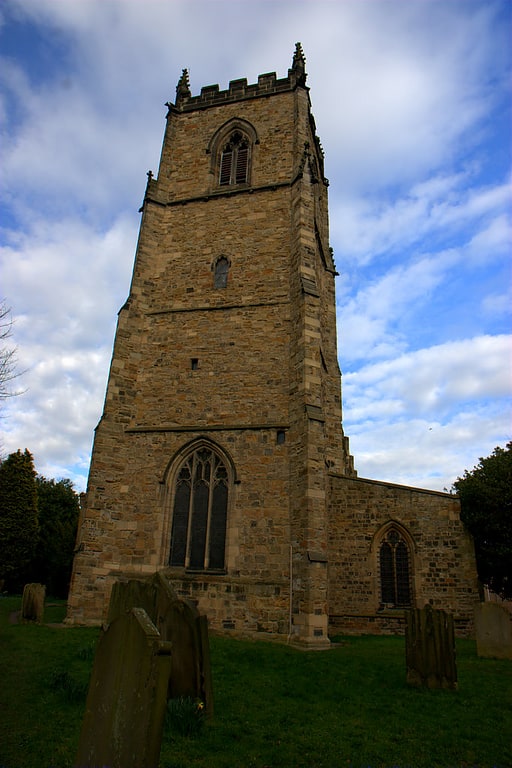

Anglican church in Durham, England. St Oswald's Church is a Church of England parish church in Durham, County Durham. The church is a grade II* listed building and it dates from the 12th century.[20]